On Saturday, UBS AG was considering a move to acquire its struggling Swiss counterpart Credit Suisse. This potential acquisition could potentially prevent the financial turmoil that could arise from the current crisis that Credit Suisse is facing.
The banking giant Credit Suisse, which is 167 years old, has been caught up in the fallout of the recent failure of two American lenders, Silicon Valley Bank and Signature Bank. This has caused a worldwide decline in investor confidence.
In an effort to revive faith in the banking sector, American and European finance professionals and watchdogs have implemented exceptional precautions. The Biden Government guaranteed client deposits, while the Swiss National Bank loaned Credit Suisse up to 50 billion Swiss Francs to maintain its unsteady financial situation.
The Swiss government is reportedly putting pressure on UBS to take over Credit Suisse as a way to address the current crisis. According to two knowledgeable sources, the government may provide a security against the associated risks while Credit Suisse’s Swiss operations could be split off.
When contacted for comment, neither UBS, Credit Suisse nor Switzerland’s financial regulator FINMA offered a response.
According to the Financial Times, sources familiar with the situation stated that the involved parties were striving to reach a merger agreement as soon as Saturday night.
American officials are participating in the process, collaborating with their Swiss associates in order to facilitate an agreement, according to the Bloomberg News report, as quoted by those knowledgeable of the circumstance.
UBS Stocks – In past 5 days UBS Stocks lose -10,44%.
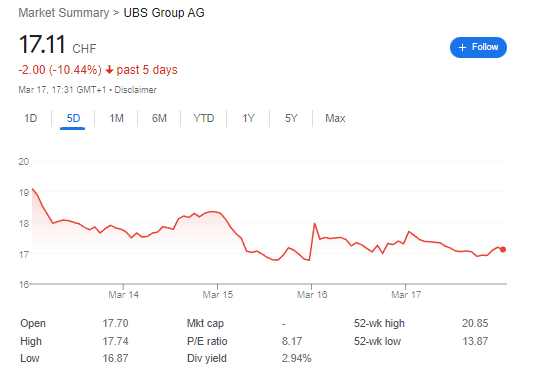
According to recent news from Zacks Equity Research, UBS Group AG was listed as the Bull of the Day on March 9, 2023. However, in the past five days, UBS stocks have reportedly lost 10.44% of their value [1]. This could be a result of Credit Suisse’s recent struggles, which have affected the overall banking sector. Short sellers of regional bank stocks are seeing windfall profits, and concerns about Credit Suisse’s material weakness have weighed on other bank stocks [2]. Additionally, UBS was one of several companies that experienced a drop in stock prices due to analyst downgrades, warnings of weak demand, and losses rather than profits [3].
References:
[1] UBS and Alico have been highlighted as Zacks Bull and Bear … [2] Regional and big bank stocks resume slide amid rising fears … [3] Pops & Drops: Hess, Alcoa… – CNBCCredit Suisse Stocks
Shares of Credit Suisse have sunk by a quarter in the past seven days due to a series of scandals which caused investors and customers to doubt the company. This then led to the first instance of a major international bank having to resort to $54 billion in central bank support since the 2008 financial crisis.
The business is placed among the world’s most extensive wealth managers and is counted among 30 global systemically significant banks whose breakdown could cause shockwaves throughout the financial system.
Lotfi Karoui, a Goldman analyst, declared in a Friday note to customers that the fundamentals of the banking sector are firmer and the connections to the global system are not as strong as they were during the 2008 economic crisis. That reduces the likelihood of a “destructive cycle of counterparty credit losses,” Karoui said.
Karoui noted that a greater effort is anticipated to be needed in order to bring about equilibrium. Additionally, the bank stated that the absence of clarity on Credit Suisse’s destiny will have an adverse effect on the overall European banking industry.
On Saturday, an authoritative representative from China’s central bank cautioned that swift rate increases in the foremost industrialized countries may have an adverse effect on the financial system.
The Risk of Changing Interest Rates
Interest rate risk is a concept that describes the possibility that interest rates may change in the future, potentially leading to losses for certain investments. This risk is especially relevant for those who invest in financial products with variable or adjustable interest rates. For example, those who invest in bonds with adjustable coupon rates may be exposed to the risk of rising interest rates, which may result in a decrease of the bond’s value. Similarly, those who invest in financial products with variable rates of return may be subject to the same risk.
Amid the recent rate hikes from major central banks, including the European Central Bank, the collapse of Silicon Valley Bank in California has brought to light the pressure that such movements can place on the banking sector. This is the second-largest bank failure in the US after Washington Mutual’s fall in 2008 during the international financial crisis.
Since the collapse of SVB, banking stocks around the world have been subject to relentless losses, with the S&P Banks index (.SPXBK) taking a hit of 22%, the most notable decrease in the two weeks after the coronavirus pandemic first rocked markets in March 2020.
Significant American financial institutions recently provided First Republic (FRC.N) with a $30 billion rescue package, while banks all over the U.S. requested an unprecedented amount of $153 billion in emergency funding from the Federal Reserve.
Moody’s recently revised its outlook on the U.S. banking system to negative, citing “funding and liquidity problems experienced by banks caused by the waning trust of depositors.”
Investors were taken aback by the revelations of the amount of emergency liquidity that First Republic Bank required, despite the support from some of the major banking players in the U.S. preventing a total meltdown.
Attention in Washington has shifted to enforcing stricter oversight in order to guarantee that banks and their leaders are subject to responsibility.
Joe Biden, the President of the United States, encouraged Congress to give more authority to the regulators with regards to the sector, such as higher fines, taking back funds, and prohibiting officials from failed banks from participating.
FAQs about Credit Suisse Banking Crisis 2023
Credit Suisse has been facing several challenges and losses, which have led to management beginning “strategic scenario” talks over the weekend [1]. The bank has reportedly received a liquidity lifeline from the Swiss National Bank after a series of losses and scandals, and there are talks of a possible takeover by UBS [1]. These developments have caused concerns about the stability of the Swiss banking sector, and the Swiss regulator Finma is reportedly involved in negotiations to boost confidence [1]. Credit Suisse has issued several media releases in recent times, including an announcement to strengthen liquidity and public tender offers for debt securities [3]. The bank has also informed on a FINMA review and an expansion of its sustainability offering for corporate clients [3].
References:
[1] Credit Suisse: Banking experts predict what could happen next
[2] Credit Suisse – latest news, breaking stories and comment
[3] Media releases – Credit Suisse
The last banking crisis, also known as the Global Financial Crisis of 2008, had a profound impact on the global economy and resulted in several lessons learned. Some of the key lessons include:
1 – The importance of risk management: The crisis highlighted the need for banks to have strong risk management systems in place to identify, monitor, and manage risks effectively.
2 – The need for transparency and accountability: The crisis exposed the lack of transparency and accountability in the banking sector, which led to a loss of confidence in financial institutions. As a result, regulatory bodies have increased their focus on transparency and accountability in the sector.
3 – The impacts of interconnectedness: The crisis demonstrated the interconnectedness of the global financial system and how the failure of one institution can have a ripple effect across the entire system.
4 – The importance of regulation: The crisis highlighted the need for effective regulation to prevent excessive risk-taking and ensure the stability of the financial system.
5 – The role of ethical behavior and corporate culture: The crisis revealed the importance of ethical behavior and a strong corporate culture in the banking sector. Banks need to prioritize ethical behavior and cultivate a culture that prioritizes responsible business practices.
Overall, the lessons learned from the last banking crisis have resulted in significant changes in the banking sector, including increased regulation, stronger risk management systems, and a greater focus on transparency and accountability.
Credit Suisse is currently facing several challenges and losses, which have led to talks about a possible sale or merger. The bank has been struggling with the aftermath of the Greensill and Archegos scandals, which have resulted in significant losses and reputational damage. As a result, the bank’s share price has fallen, and there are concerns about the stability of the Swiss banking sector.
While there have been talks of a possible sale or merger with another bank, such as UBS, it is not clear if this will happen. Credit Suisse’s management has stated that they are committed to turning the bank around and restoring confidence in the institution. They have announced several measures to strengthen liquidity and improve risk management systems, and are working with regulators to address the issues facing the bank.
Overall, it is too early to say whether Credit Suisse will fail or be sold. The bank is facing significant challenges, but it has a strong brand and reputation, and its management is committed to addressing the issues facing the institution.


