When it comes to the cost of food, the prices of groceries and other consumables can be affected by food inflation. Inflation is a natural part of the economy and it is something that must be monitored and managed in order to ensure that prices remain stable. This article will explore what food inflation is, the causes of it, and the effects it can have on the economy. We will also look at historical trends, factors that can determine food inflation, practical strategies to deal with it, and government policies to reduce it.
Also read: Americans Show Optimism as Inflation Eases and Economy Recovers.
What is food inflation?
Food inflation is the process of rising prices for food products due to various factors such as supply and demand, economic policies, and the cost of production. This rise in prices can have an effect on the economy as it can cause an increase in the cost of living and force people to spend more money on food. Inflation is measured by the Consumer Price Index (CPI), which looks at the changes in price of a basket of goods and services over time.
When food inflation is high, it means that the cost of food is rising faster than the average rate of inflation. This can be a problem for many households as it means that their purchasing power is reduced. This can be especially difficult for those on lower incomes as they may not be able to afford the basic necessities.
Read also this FintechZoom article: What is a Recession? Unveiling the Difference Between Inflation Vs Recession!
Causes of food inflation
There are many factors that can lead to food inflation, but some of the main ones are:
- Supply and demand: When demand for food is higher than the available supply, this can cause prices to rise. This can happen due to increased population growth, changes in dietary preferences, or a shortage of supply due to bad weather.
- Economic policies: Government policies such as increasing taxes on food products can cause prices to rise. This can also lead to higher prices for commodities such as oil and other inputs used to produce food.
- Cost of production: The cost of producing food can increase due to higher costs of inputs such as fertilizers, pesticides, and labor. This can also be affected by environmental changes such as climate change.
- Currency exchange rates: If the value of a country’s currency decreases compared to other currencies, this can lead to higher prices for food imported from other countries.
COVID-19 and Food Price Inflation
The COVID-19 pandemic has had a devastating impact on global food prices and food security, leading to a dramatic rise in poverty in many parts of the world. [1] In January 2023, the CPI for all food increased 0.7 percent from December 2022 to January 2023, and food prices were 10.1 percent higher than in January 2022. [2] Food prices are expected to grow more slowly in 2023 than in 2022, but still at above historical average rates. In 2023, all food prices are predicted to increase 7.9 percent, with a prediction interval of 5.5 to 10.3 percent. [3]
This rapid increase in food prices has caused a significant increase in global poverty, with the World Bank estimating that the pandemic could push an additional 88 million people into extreme poverty in 2020. [4] In addition, food insecurity has risen dramatically, with the World Food Programme estimating that an additional 130 million people could suffer from hunger in 2021. [5]
The impact of this food price inflation has been particularly severe in developing countries, where many people already live on low incomes and have limited access to nutritious food. [6] Governments around the world have taken steps to counter the effects of the pandemic, but it is clear that the impact of the pandemic on global poverty and food security will be felt for years to come.
References:
[1] Summary Findings – USDA ERS [2] COVID-19 and rising global food prices: What’s really … – IFPRI [3] The impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on food price indexes …Ukraine Russia War and Food Price Inflation
The ongoing conflict between Russia and Ukraine is not only a political and military struggle, but also a humanitarian crisis that has resulted in widespread food insecurity. [1] The three-year war has resulted in a dramatic rise in food prices in Ukraine, with the cost of basic commodities such as flour and sugar increasing by more than 40% in 2023. [2] This price increase has had a devastating effect on food security in Ukraine, with more than 4 million people estimated to be in need of emergency food assistance. [3]
The conflict has also had a major impact on the agricultural sector, with more than two million hectares of farmland being destroyed or made unusable due to the war. [4] The impact of the war has been felt beyond Ukraine’s borders, with the conflict having an impact on global food prices as well. [5] Research from Goldman Sachs suggests that the disruption of food production in Ukraine and Russia has caused prices to rise significantly. [6]
Read also this FintechZoom article: Could it be that both inflation and the equity market are peaking at about the same time?
In addition, the war has disrupted supply chain distribution and caused input prices to increase, putting pressure on global food inflation. [7] The conflict in Ukraine is far from over, and the food security crisis is likely to worsen in the coming years. [8] It is therefore essential that solutions are found to address the food insecurity crisis, and that countries around the world work together to ensure that the conflict does not have a lasting impact on global food prices. [9]
References:
[1] How is the war in Ukraine affecting global food prices? [2] The War in Ukraine Stokes Global Food Inflation [3] Food Prices by War in Ukraine | IFPRIEffects of food inflation
The effects of food inflation can be wide-reaching and can have a negative impact on the economy. Some of the most notable effects include:
- Decrease in purchasing power: As prices rise, people may find it more difficult to afford basic necessities such as food and other items. This can be especially difficult for those on low incomes.
- Increase in poverty: As food prices rise, people may be forced to choose between buying food and other necessities. This can lead to an increase in poverty levels and can have a long-term effect on the economy.
- Inequality: When food prices rise, those on lower incomes may be disproportionately affected. This can lead to a widening of the wealth gap and further inequality in society.
- Reduced savings: Rising food prices can lead to people having to use up their savings in order to buy food, leading to a decrease in their financial security.
Is the poverty increased due Food Inflation?
Yes, food inflation has had a significant impact on poverty levels around the world. When food prices increase, the cost of living rises, and those living in poverty often struggle to keep up. This can result in a decrease in disposable income, which can further exacerbate poverty levels. Furthermore, food inflation often leads to a decrease in the purchasing power of individuals, which can lead to an increase in poverty. The increase in poverty is particularly acute in developing countries, where access to food is often limited and poverty levels are already high.
Additionally, food inflation can have a negative impact on other sectors of the economy, such as the manufacturing and service industries, which can further add to poverty levels. In order to combat poverty caused by food price inflation, governments and international organizations must work together to develop policy solutions that make food more accessible and affordable, and ensure that there is an adequate safety net in place to protect those most vulnerable to the effects of food price inflation.
Exploring the impact of food inflation on the economy
Food inflation can have a negative impact on the economy as it can lead to a decrease in purchasing power and an increase in poverty levels. This can lead to a decrease in consumer spending, which can have a damaging effect on GDP growth. It can also lead to an increase in government spending as they may need to provide more assistance to those affected by the rising cost of food.
Food inflation can also have a negative effect on businesses, as it can reduce their profits due to higher costs of production. This can lead to businesses having to cut back on their workforce or reduce the wages of their employees. This can have a long-term effect on the economy, as it can lead to a decrease in consumer spending and an increase in unemployment.
Historical trends in food inflation
Food inflation has been a problem for many countries for many years, and it is important to look at historical trends in order to analyze the current state of food prices. In the United States, food inflation reached its highest level in 2008 at 6.2%. This was due to a combination of factors such as rising fuel prices, the global financial crisis, and an increase in demand for food.
Since then, food inflation has been relatively stable, fluctuating between 1.4% and 3.5%. This is due to a number of factors such as government policies, currency exchange rates, and the cost of production.
According to Food price monitoring tool from Eurostat, the Food price increased 18.4% in January 2023.
According to Food price monitoring tool from Eurostat, the Food price increased 18.4% in January 2023.
According to the Eurostat food price monitoring tool [2], food prices increased by 18.4% in January 2023. This is a significant increase compared to the previous month of December 2022, when food prices increased by around 14.1%. This sharp increase in food prices can be attributed to a number of factors, including the ongoing conflict between Russia and Ukraine, which has disrupted global supply chains and caused prices to rise. Additionally, the Eurozone inflation rate fell to 8.5% in January 2023, down from 9.2% in December 2022, which could have also contributed to the sharp increase in food prices. This increase in food prices can be a cause for concern, as it is likely to have a negative impact on those living in poverty, who are likely to struggle to keep up with the rising costs of living
References:
[1] Eurozone inflation dropped for a third month. Which countries … [2] Food price inflation: interactive visualisation tool – Eurostat [3] Eurozone inflation slows to 8.5% in January: Eurostat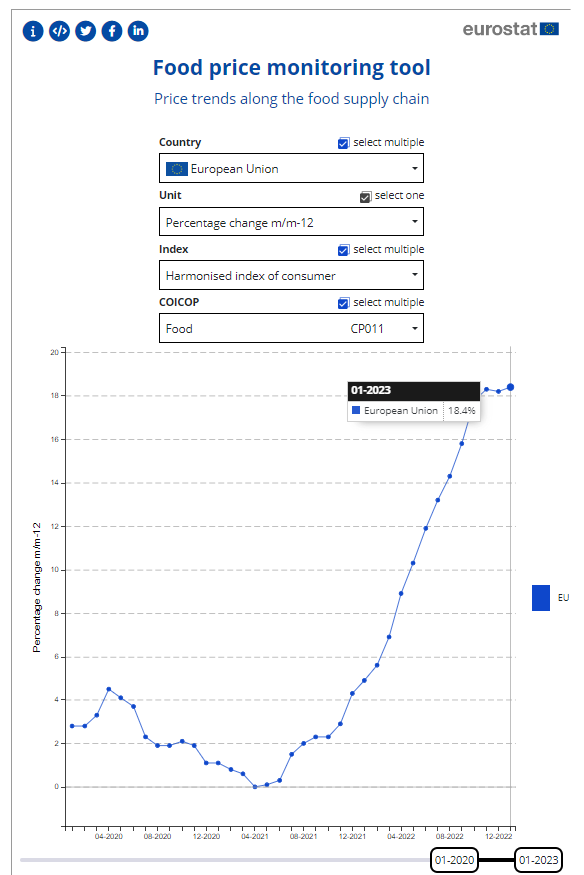
Food Inflation in G20 Countries
Food Inflation in G20 Countries – Turkey has in January 2023 77.87%, UK 16.8% and USA 10.4%.
According to the data from the web search results [1], the food inflation rate in Turkey in January 2023 was 77.87%, the highest in the G20. This was followed by the United Kingdom, where the food inflation rate was 16.8%, and the United States, where it was 10.4%. It is clear that the food inflation rate in Turkey is dramatically higher than in the other G20 countries, likely due to the economic mismanagement and political instability in the country. Additionally, the import-dependent nature of the Turkish economy may be a factor in the high level of food inflation.
To combat this, the Turkish government must take effective measures to improve the economy, such as implementing market-accepted government policies and raising interest rates. Additionally, international organizations can help by providing aid and resources to those affected by the high food inflation
References:
[1] Food Inflation – Countries – List – Trading Economics [2] These countries have been the hardest hit by food price inflation [3] Which countries have the highest levels of inflation in 2023?| Country | Last | Previous | Reference | Unit |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Argentina | 98.4 | 95 | Jan/23 | % |
| Australia | 9.2 | 9 | Dec/22 | % |
| Brazil | 11.07 | 11.64 | Jan/23 | % |
| Canada | 10.4 | 10.1 | Jan/23 | % |
| China | 6.2 | 4.8 | Jan/23 | % |
| Euro Area | 16.3 | 16 | Jan/23 | % |
| France | 14.5 | 13.3 | Feb/23 | % |
| Germany | 19.2 | 19.4 | Jan/23 | % |
| India | 5.94 | 4.19 | Jan/23 | % |
| Indonesia | 5.82 | 5.83 | Jan/23 | % |
| Italy | 12.8 | 13.1 | Jan/23 | % |
| Japan | 7.3 | 7 | Jan/23 | % |
| Mexico | 12.77 | 12.7 | Jan/23 | % |
| Netherlands | 17.3 | 16.8 | Jan/23 | % |
| Russia | 10.16 | 10.3 | Jan/23 | % |
| Saudi Arabia | 4.24 | 4.17 | Jan/23 | % |
| Singapore | 8.1 | 7.5 | Jan/23 | % |
| South Africa | 13.4 | 12.4 | Jan/23 | % |
| South Korea | 5.77 | 5.23 | Jan/23 | % |
| Spain | 15.35 | 15.69 | Jan/23 | % |
| Switzerland | 5.6 | 4 | Jan/23 | % |
| Turkey | 71 | 77.87 | Jan/23 | % |
| United Kingdom | 16.7 | 16.8 | Jan/23 | % |
| United States | 10.1 | 10.4 | Jan/23 | % |
Factors determining food inflation
There are a number of factors that can affect food inflation, such as supply and demand, economic policies, and the cost of production. It is important to understand these factors in order to understand why food prices are rising and what can be done to reduce them.
- Supply and demand: When demand for food is higher than supply, this can lead to higher prices. This can be caused by population growth, changes in dietary preferences, or a decrease in supply due to bad weather.
- Economic policies: Government policies such as increasing taxes on food can lead to higher prices. This can also be affected by global economic policies such as currency exchange rates.
- Cost of production: The cost of producing food can increase due to higher costs of inputs such as fertilizers, pesticides, and labor. This can also be affected by environmental changes such as climate change.
Practical strategies to deal with food inflation
It is important to understand the causes of food inflation in order to know how to deal with it. There are a number of strategies that can be used to reduce food prices, such as:
- Increasing production: One way to reduce food prices is to increase the supply of food. This can be done by increasing the use of fertilizer, pesticides, and other inputs. It can also be done by adopting new technologies and increasing the productivity of farms.
- Reducing taxes: Reducing taxes on food products can help to reduce prices. This can be done by reducing taxes on inputs such as fertilizer and pesticides, or by lowering import taxes on food products.
- Improving storage: Improving storage facilities can help to reduce food waste, which can lead to lower prices. This can be done by investing in new technologies such as refrigeration and better storage facilities.
- Strengthening regulation: Strengthening regulation on food prices can help to ensure that prices remain stable. This can be done by setting limits on prices and ensuring that these limits are enforced.
Government policies to reduce food inflation
In order to reduce the effects of food inflation, governments need to implement policies that can help to reduce prices and ensure that food is affordable for everyone. Some of the most common policies used to reduce food prices include:
- Subsidies: Governments can provide subsidies to farmers in order to reduce the cost of production. This can help to reduce prices and make food more affordable.
- Price control: Governments can set price limits on food products in order to ensure that prices remain stable. This can help to reduce food inflation and make food more affordable.
- Trade agreements: Governments can enter into trade agreements with other countries in order to reduce the cost of imports. This can help to reduce food inflation and ensure that prices remain stable.
FAQs about Food Inflation
Food inflation is an economic term used to describe the increase in the price of food over a period of time. It is usually measured by the Consumer Price Index (CPI). This index is used to measure the average prices of food items across the country.
Food inflation is measured by the Consumer Price Index (CPI). This index is used to measure the average prices of food items across the country. The CPI is calculated using a basket of goods and services that reflects the average household’s purchase pattern. The prices of these items are tracked over time to measure inflation.
There are several factors that can lead to food inflation. These include weather conditions, supply and demand, population growth, and government policies. Weather conditions can affect the supply of food, and when supply is low, prices tend to rise. Supply and demand also affects food prices, as when demand increases, prices tend to rise to meet the increased demand. Population growth can also affect food prices, as increased demand for food means higher prices. Government policies can also affect food prices, as taxes and subsidies can alter the supply and demand of food.
The effects of food inflation can be felt by individuals and by the economy as a whole. At the individual level, food inflation leads to higher food costs, which can put a strain on households. Higher food costs reduce the amount of disposable income that households have, limiting their ability to purchase other goods and services. At the macroeconomic level, food inflation can lead to increased costs for businesses and government.
Conclusion
Food inflation is a natural part of the economy and it is important to understand the causes and effects of it in order to ensure that prices remain stable. There are a number of factors that can affect food prices, such as supply and demand, economic policies, and the cost of production. It is also important to understand the historical trends in order to analyze the current state of food inflation.
In order to reduce food inflation, there are a number of strategies that can be used such as increasing production, reducing taxes, improving storage, and strengthening regulation. Governments can also implement policies such as subsidies, price control, and trade agreements in order to reduce food prices.
Food inflation can have a negative impact on the economy, but with the right strategies and policies in place, it can be managed and reduced. Understanding the causes and effects of food inflation is essential in order to ensure that prices remain stable and that everyone has access to affordable food.


