As the world continues to grapple with the Covid-19 pandemic, one of the countries that has been particularly affected is China. The virus first appeared in the city of Wuhan, China, in the latter half of 2019 and quickly spread throughout the country, prompting the Chinese government to take swift and decisive action in order to contain the virus. In this blog article, we will take a deeper look into the impact of China Covid on the country and its people, as well as how the Chinese government has responded to the crisis.
Introduction to China Covid
The Covid-19 pandemic has had an unprecedented impact on the world, with few countries being as affected as China. The virus first appeared in the city of Wuhan in late 2019 and quickly spread throughout the country, prompting the Chinese government to take swift and decisive action in order to contain the virus.
In the early days of the outbreak, the Chinese government took drastic measures to contain the virus, including sealing off cities, implementing travel restrictions, and canceling public events. In addition, the Chinese government implemented a strict quarantine regime, requiring all citizens to wear masks and practice social distancing.
Despite these measures, the virus continued to spread throughout the country. As a result, the Chinese government was forced to take further action in order to contain the virus, including ordering all citizens to stay home and shutting down many businesses.
Overview of the Covid Outbreak in China
The Covid-19 outbreak in China has had a profound impact on the country and its people. According to the latest statistics, there have been more than 85,000 confirmed cases of Covid-19 in China, with over 4,600 deaths.
The outbreak has had a far-reaching impact, with the virus spreading rapidly throughout the country and affecting people from all walks of life. In addition, the Chinese government has been forced to implement strict measures in order to contain the virus, including travel restrictions, social distancing, and quarantine regimes.
These measures have had a profound impact on the Chinese economy, with many businesses forced to close down and millions of people out of work. In addition, the outbreak has caused disruption to the country’s health care system, with hospitals and clinics struggling to cope with the influx of patients.
Economic and Social Impact of the Outbreak
The economic and social impact of the Covid-19 outbreak in China has been profound. According to the latest figures, the outbreak has cost the Chinese economy more than $3 trillion in lost GDP, with millions of people out of work and businesses struggling to survive.
The outbreak has also had a profound impact on the social fabric of the country, with people being forced to stay home and socialize only with members of their own family. In addition, people have been forced to wear masks and practice social distancing whenever they are out in public.
The outbreak has also led to a rise in anxiety and depression among the population, with many people feeling isolated and unable to cope with the situation. In addition, the lockdown has caused disruption to the education system, with many students unable to attend school due to the travel restrictions.
How China Responded to the Outbreak
In response to the Covid-19 outbreak, the Chinese government took swift and decisive action in order to contain the virus. The government implemented a strict quarantine regime in order to contain the spread of the virus, with travel restrictions, mandatory mask-wearing, and social distancing measures.
In addition, the Chinese government took a number of steps to support affected businesses, such as providing tax relief and financial support to those who have been affected by the outbreak. The government also rolled out a number of initiatives to support those who have been laid off due to the pandemic, such as offering job training and retraining programs.
The Chinese government also launched an aggressive public awareness campaign in order to educate people about the virus and how to protect themselves. In addition, the government launched a number of initiatives aimed at preventing the spread of the virus, such as contact tracing and testing.
Health System Performance and Challenges
The outbreak of Covid-19 in China has had a profound impact on the country’s health care system. The outbreak has caused an influx of patients to hospitals and clinics, with many hospitals struggling to cope with the influx.
In addition, the outbreak has caused a shortage of medical supplies, with many hospitals and clinics lacking the necessary equipment and resources to treat patients. The outbreak has also caused a shortage of doctors and nurses, with many of them being redeployed to other parts of the country in order to contain the virus.
The outbreak has also caused disruption to the country’s health insurance system, with many people struggling to access the care they need due to the high cost of health care. In addition, the outbreak has caused a decrease in the number of people seeking medical care due to fears of contracting the virus.
Government Policies and Initiatives to Address the Outbreak
In response to the outbreak, the Chinese government has implemented a number of policies and initiatives in order to contain the virus and mitigate its impact. The government has implemented a strict quarantine regime, requiring all citizens to wear masks and practice social distancing.
In addition, the government has rolled out a number of initiatives to support those affected by the outbreak, such as providing tax relief and financial support to those who have been laid off due to the pandemic. The government has also implemented a number of measures to prevent the spread of the virus, such as contact tracing and testing.
The government has also launched an aggressive public awareness campaign in order to educate people about the virus and how to protect themselves. In addition, the government has provided free health care to those affected by the virus and has implemented a number of measures to support the country’s health care system, such as providing additional resources and personnel.
Challenges for the Chinese Government
Despite the Chinese government’s efforts to contain the virus, there are still a number of challenges that it faces. One of the biggest challenges is the lack of public trust in the government, with many people feeling that the government is not doing enough to contain the virus.
In addition, there is a lack of public understanding about the virus and how to protect themselves, with many people ignoring the government’s advice and refusing to practice social distancing or wear masks. The outbreak has also caused a shortage of medical supplies, with many hospitals and clinics lacking the necessary equipment and resources to treat patients.
The outbreak has also caused disruption to the country’s health care system, with many people struggling to access the care they need due to the high cost of health care. In addition, the outbreak has caused a decrease in the number of people seeking medical care due to fears of contracting the virus.
Impact on International Relations
The Covid-19 outbreak in China has had a profound impact on the country’s relations with the rest of the world. The outbreak has caused a strain on the country’s relationship with the US, with the two countries trading accusations and accusations of the other’s handling of the virus.
In addition, the outbreak has caused disruption to the global economy, with many countries facing economic hardship due to the outbreak. The outbreak has also caused disruption to global supply chains, with many companies struggling to meet customer demand due to the shortage of goods.
The outbreak has also caused a strain on the country’s relationship with its neighbors, with some countries accusing China of not doing enough to contain the virus. In addition, the outbreak has caused a strain on the country’s relationship with the international community, with many countries accusing China of not being transparent about the outbreak.
The surge in China’s VoIP market has hit both factories and the consumer market.
A wave of Covid cases is sweeping across China, putting the country’s economy under severe strain.
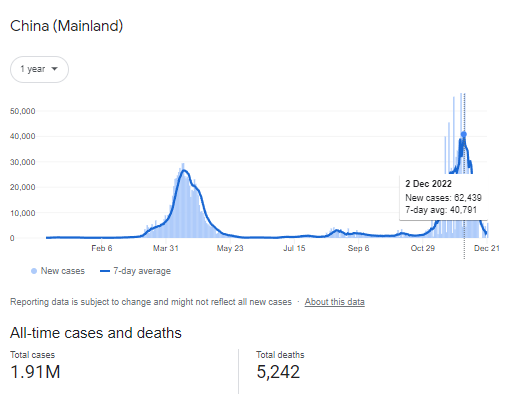
Since the world’s second largest economy drastically eased its Covid restrictions earlier this month, there has been no clear data on the extent of the virus’ spread on the national level. However, several cities and provinces have said they were seeing tens of thousands of new cases daily.
Many people have been driven indoors and businesses and restaurants have been emptied as a result of the rapid spread of infection. Businesses and factories, in turn, have been forced to close down or reduce production owing to an increase in sick workers.
According to analysts from Capital Economics, the reduction in people on the streets across the country has been dramatic. That, they say, will have an adverse impact on demand.

China’s economy was already struggling when Beijing abandoned its strict zero-Covid policy. Retail sales had declined in November because of widespread lockdowns, and unemployment had reached its highest level in six months.
Senior officials recently have said that they will focus on growth again next year and have bet on the lifting of pandemic restriction to boost the economy.
People walk past closed stores at a shopping mall amid the COVID-19 outbreak, ahead of the Christmas holiday, in Shanghai, China December 23, 2022.
Unfortunately, the numbers are not in our favour.
According to the China Passenger Car Association, vehicle sales between December 1 and December 18 were down 15% compared to the same period last year. Home sales in 30 major cities decreased 44% last week, according to Chinese financial data provider Wind. In cities such as Beijing and Shanghai, home sales decreased 53% from a year ago, last week.
- People’s participation in movements has also declined.
- In the major cities, the number of subway trips has dropped 60% since the middle of this month, according to Wind data.
- The transportation ministry and the postal service regulator reported that trucking volumes and delivery orders had both fallen nationwide.
- Cement and chemical fibre production have both reported lower utilisation rates of their existing production capacity in factories.
Because more workers are unable to work, BYD, the country’s largest electric vehicle manufacturer, said it had to cut production by 2,000 to 3,000 vehicles per day.
Lian Yubo, BYD’s vice president, said at a forum in Shenzhen yesterday that Covid’s outbreak has severely impacted our production. Up to 30% of our employees are home sick, he said.
Production for December is likely to fall short of target by 20,000 to 30,000 vehicles, he said.
Reports say that many factories have been forced to shut down because workers are sick and because orders are low.
Employees at several furniture plants in eastern Jiangsu province were told to take an early, long vacation to celebrate the Chinese New Year, Caixin reported Monday. The Lunar New Year holiday will last from January 21 to January 27 this year.
In the coastal provinces of Guangdong, Zhejiang, and Shandong—China’s main manufacturing hubs—as many as 60% of textile and dyeing businesses have said they would halt production for two months, according to a state-owned Henan Daily Press Group newspaper, the Securities Daily.
China’s battle with Covid may be “the most dangerous” over the next few weeks, according to Capital Economics analysts.
“Prior to Lunar New Year celebrations beginning, a large number of people are expected to move to rural areas,” they said.
If firms reduce production, output will be even more depressed.
Conclusions
The Covid-19 outbreak in China has had a profound impact on the country and its people. The outbreak has caused disruption to the economy, with millions of people out of work and businesses struggling to survive.
In addition, the outbreak has caused disruption to the health care system, with hospitals and clinics struggling to cope with the influx of patients. The outbreak has also caused a strain on the country’s relationship with the rest of the world, with many countries accusing China of not doing enough to contain the virus.
The Chinese government has responded to the outbreak with swift and decisive action, implementing a number of measures to contain the virus and mitigate its impact. However, there are still a number of challenges that the government faces, including a lack of public trust and understanding, a shortage of medical supplies, and disruption to the health care system.
Recommendations for the Future
In order to address the challenges posed by the Covid-19 outbreak in China, the Chinese government should take a number of steps. First, the government should focus on improving public trust in the government and its handling of the outbreak, by providing clear and transparent information about the outbreak and its containment measures.
Second, the government should focus on improving access to health care, by providing free health care to those affected by the virus and increasing the availability of medical supplies and personnel.
Third, the government should focus on improving the country’s relationship with the international community, by providing clear information about the outbreak and its containment measures and engaging in dialogue with other countries.
Finally, the government should focus on investing in the future, by investing in research and development and providing incentives for businesses to innovate and create new jobs.
By taking these steps, the Chinese government can address the challenges posed by the Covid-19 outbreak and ensure that the country is better prepared for future health crises.
China Covid has had an unprecedented impact on the country and its people, with the Chinese government taking swift and decisive action in order to contain the virus. Despite these efforts, the outbreak has caused disruption to the economy, the health care system, and the country’s relationship with the rest of the world. Going forward, the Chinese government should focus on improving public trust, access to health care, the country’s relationship with the international community, and investing in the future in order to ensure the country is better prepared for future health crises.


