The price earnings ratio, often abbreviated as the P/E ratio, is a measure of how much investors are willing to pay for each dollar of a company’s earnings. In other words, it is a calculation that shows you how much you would have to spend on a share of stock in order to receive one dollar of that company’s annual earnings. This number can be helpful when you are trying to decide if a stock is overpriced or not. If the P/E ratio is high, it means that investors are expecting big things from the company in the future and that the stock may be overpriced. On the other hand, if the P/E ratio is low, it may mean that the stock is undervalued and
What is price earnings ratio?
The price earnings ratio, often abbreviated as the P/E ratio, is a measure of how much investors are willing to pay for each dollar of a company’s earnings. In other words, it compares the current market value of a stock to its per-share earnings.
To calculate the P/E ratio, you simply take the stock’s current market price and divide it by its per-share earnings.
While this can be an effective way to compare different stocks in different industries, there are some considerations to keep in mind when using this metric. For example, a company that has very high growth potential may have a relatively high cost in order to secure a share of its stock. Additionally, companies with net losses may have zero or even negative per-share earnings and thus will have an undefined P/E ratio. Despite these limitations, the price earnings ratio remains one of the most widely used tools for evaluating stocks and company performance.
What is Price Earnings Ratio Formula?
The price earnings ratio formula, or P/E ratio for short, is a common valuation metric used to measure the relative value of different stocks. This ratio is calculated by dividing the current market price of a stock by its earnings per share.
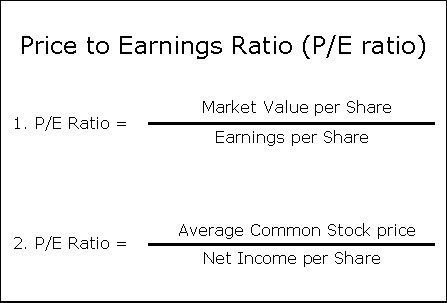
In essence, it measures how much investors are willing to pay for each dollar of a company’s earnings. The higher the P/E, the more investors are willing to pay for each dollar of a company’s profit.
While this metric can be useful in comparing different companies and industries, it should be used only as one piece of information and should never be taken as definitive proof that one stock is necessarily better than another. Nevertheless, understanding and using the P/E ratio formula can help investors make informed decisions about their investment portfolio.
Companies with a high Price Earnings Ratio
Companies with a high price to earnings ratio tend to be those that are considered to be of high quality and value. These companies typically have strong profit margins, sustainable revenue streams, and healthy balance sheets. Are often considered to be growth stocks.
This makes them attractive investment opportunities for many investors, since they tend to perform well in both the short and long term. Additionally, investors who wish to minimize their risk may choose to invest in companies with high price to earnings ratios, as these firms tend to be less volatile and more stable than those with lower ratios. Ultimately, companies with a high price earnings ratio are seen as positive investments by many investors and analysts alike, as they exemplify the best qualities of successful businesses.
Companies with a low Price Earnings Ratio
A low Price Earnings Ratio (or PE ratio) is often seen as a sign of strength and stability in a company. This is because the ratio reflects how well a company’s stock price compares to its earnings, with higher numbers indicating higher profitability.
Generally speaking, companies with lower PE ratios are thought to be more valuable and reliable investments, since they are able to generate stable profits for shareholders. A number of factors can influence a company’s PE ratio, including growth potential, competition from similar businesses, and the overall health of the economy. Overall, though, low PE ratios are viewed as a sign of quality in modern business, making them an appealing choice for investors looking to maximize their returns.
What is a good earnings price ratio?
There is no single “correct” earnings price ratio, as the ideal ratio will depend on a number of different factors. For example, the industry in which a company operates can have a significant impact on its earnings price ratio. In a highly competitive field with many similar businesses, a higher earnings price ratio may be more appropriate; this will indicate that the company is able to maintain good profit margins despite intense competition. On the other hand, companies operating in less competitive industries may be better suited for lower ratios, since they are able to generate relatively high profits even when offering discounts or sales. Ultimately, finding the right range for an earnings price ratio requires carefully considering both individual companies and overall market trends.
In order to understand how value investing works, it is helpful to have a sense of what the average P/E ratio for the market typically looks like. Many experienced value investors believe that a P/E ratio between 20 and 25 is typical for the market overall, though there is naturally some variation depending on factors such as industry sector and economic conditions. By choosing companies with P/E ratios that are lower than these average levels, you can reduce your risk of buying overvalued stocks while still capturing many of the benefits of investing in the market. At the same time, it is important to remember that this type of analysis is only one tool among many that should be used as part of an overall investment strategy. Ultimately, it is up to individual investors to determine which approach makes the most sense for their unique financial situation.
What does a high PE ratio mean?
A high PE ratio is generally used as a measure of a company’s financial health. This ratio compares the price of a stock to its earnings per share, or EPS. If a company has a high PE ratio, it means that investors are expecting strong growth in the future, forecasting increased profits and higher stock prices. Conversely, if a company has a low PE ratio, it suggests that investors believe the company’s performance will be weaker in the near future. As such, having a high PE ratio can be seen as an indicator of financial strength and success, whereas having a low PE ratio may suggest that the company is facing difficulties or struggling to stay competitive. Overall, understanding what a high PE ratio means is essential for anyone who wants to make informed investment decisions about companies and stocks.
Video Explanation of the Price Earnings Ratio
Conclusion
The price earnings ratio, or P/E ratio, is one of the most important metrics used by investors to evaluate the performance of a company. This ratio compares the current share price of a stock with its earnings per share, and it is used to gauge relative value and potential profit. Generally speaking, a high P/E ratio indicates that the stock may be overvalued and that there may be less room for growth. Conversely, a low P/E ratio may indicate that the stock is undervalued and represents an attractive investment opportunity. By assessing the price earnings ratio of a company, you can make more informed investment decisions and potentially make money in today’s competitive marketplace.


