The Dow Jones Industrial Average (DJIA) is a price-weighted average of 30 significant stocks traded on the New York Stock Exchange and the NASDAQ. The DJIA was created by Charles Dow in 1896. The DJIA has been calculated daily since May 26, 1897. It is the second oldest U.S. market index after the Dow Jones Transportation Average, which was also created by Dow. In this article, we’ll take a detailed look at the Dow Jones Industrial Average, including its components, history, and how it’s calculated. So, let’s get started!
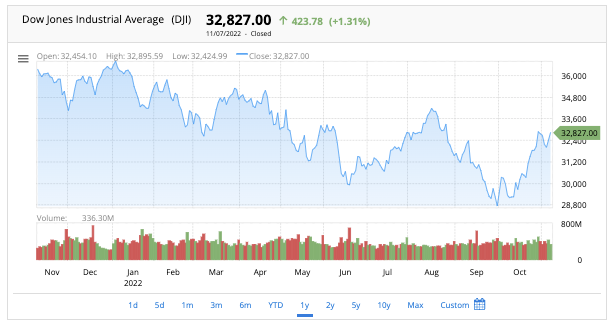
DJIA Chart Live
Check here the Dow Jones Industrial Average (INDEXDJX: .DJI) live chart:
How It’s Calculated?
The Dow Jones Industrial Average (DJIA) is one of the most closely watched indicators of the stock market. But how is it calculated? The DJIA is a price-weighted index, which means that it is calculated by taking the average of the prices of the 30 stocks that make up the index. The weights of each stock are determined by its price per share. For example, if Stock A has a price per share of $100 and Stock B has a price per share of $50, then Stock A will have twice the weight of Stock B in the DJIA.
This system gives more expensive stocks a greater impact on the index. To calculate the DJIA data, you simply add up the content prices of all 30 stocks and divide by 30 pm. Although it’s a relatively simple calculation, the DJIA is an important tool for investors to track the overall performance of the stock market. Thanks to its consistency and long history, the DJIA is one of the most widely used market indices in the world.
The 30 stocks that make up the DJIA are selected by the editors of The Wall Street Journal. These stocks are chosen based on their market capitalization, et, liquidity, and sector representation. Some of the most iconic and well-known companies are included in the DJIA, such as Coca-Cola, IBM, and Walmart. The inclusion of these companies in the DJIA reflects their importance to the U.S. economy.
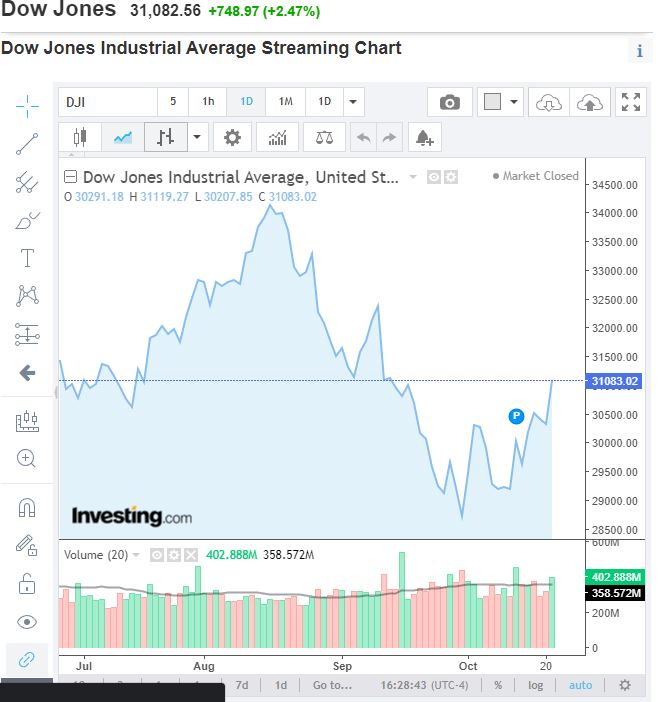
How to read a Dow Jones Industrial Average chart?
There are a few things to keep in mind when reading a DJIA chart.
1. Look at the price trend
The first thing you’ll want to do is take a look at the overall price trend. Is the market going up, down, or sideways? This will give you a good idea of the general direction of the market.
2. Identify support and resistance levels
Next, you’ll want to identify any important support and resistance levels. These are price levels where the market has a tendency to reverse direction. By identifying these levels, you can make better-informed trading decisions.
3. Look for chart patterns
Finally, you’ll want to look for any chart patterns that may be forming. These patterns can give you clues about where the market is heading next.
These are just a few things to keep in mind when reading a DJIA chart. By taking the time to understand how the index is calculated and how to read its charts, you’ll be better prepared to make informed investment decisions.
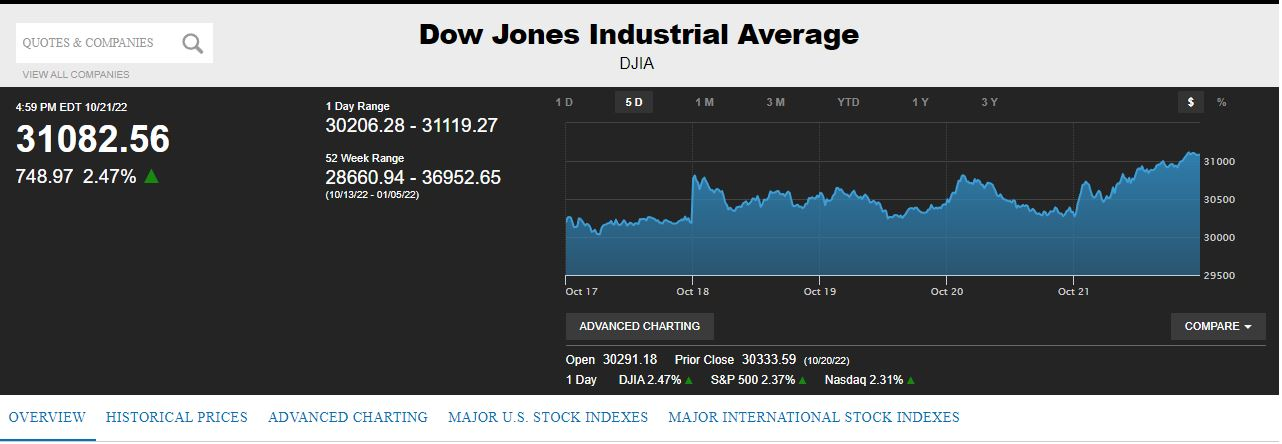
What affects the Dow Jones Industrial Average?
There are a number of factors that can affect the DJIA. These include:
1. The overall health of the US economy
The Dow is a stock market index and, therefore, is influenced by the performance of the US economy. If the economy is doing well, investors will be more confident and will be more likely to invest in stocks, driving up stock prices. Conversely, if the economy is struggling, investors will be more cautious, and stock prices will fall.
2. The performance of the US stock market
The DJIA is a US stock market index, so it is also influenced by the performance of the US stock market as a whole. If US stocks are doing well, the Dow will generally rise. If US stocks are struggling, the Dow will generally fall.
3. The performance of global stock markets
The DJIA is also influenced by the performance of global stock markets. If global stock markets are doing well, investors will be more confident on the trading day and will be more likely to invest in US stocks, driving up stock prices. Conversely, if global stock markets are struggling, investors will be more cautious, and US stock prices will fall.
4. The performance of the US dollar
DJIA is also influenced by the performance of the US dollar. When the dollar is strong, DJIA falls because it becomes more expensive for foreign investors to buy US stocks. When the dollar is weak, DJIA rises because foreign investors can buy more US stocks with their currency.
5. Interest rates
Changes in interest rates can also affect DJIA. When interest rates are low, it is cheaper for companies to borrow money, which can help to drive up stock prices. When interest rates are high, it is more expensive for companies to borrow money, which can lead to falling stock prices.
6. Political events
Political events can also affect DJIA. For example, if there is a lot of political uncertainty which can be found in the news worldwide, investors may be more cautious and may not want to invest in stocks. This can lead to falling stock prices.
7. Geopolitical events
DJIA can also be affected by geopolitical events. For example, the 2016 United States presidential election caused a sharp drop in the average as investors feared an increase in trade barriers. The 2019–20 coronavirus pandemic caused another sharp drop as businesses closed and people stayed home to prevent the spread of the virus.
These are just some of the factors that can affect DJIA. It is important to remember that the index is a long-term measure, and short-term fluctuations are to be expected. Over time, the Dow will continue to be influenced by all of these provided factors and more.
Final Thoughts
Now that you know how the Dow Jones Industrial Average is calculated and how to read its charts, you’ll be better prepared to make informed investment decisions. Remember to keep an eye on all of the factors that can affect the index, and don’t get too caught up in short-term fluctuations. With a little time and practice, you’ll be reading DJIA charts like a pro this October!


